Publication date: | Update date: 04-01-2024 | Author: Mateusz Ciećwierz
What is texture in graphics and how to create it?
In the world of computer graphics, texture is one of the key elements that gives objects realism and depth. Textures are used to simulate the appearance and feel of various materials, from smooth metal surfaces to rough fabrics. Understanding and mastering the creation of textures is essential for achieving professional visualization results. In this article, we will examine what texture in graphics exactly means and how it can be created.

Index
Definition of Texture
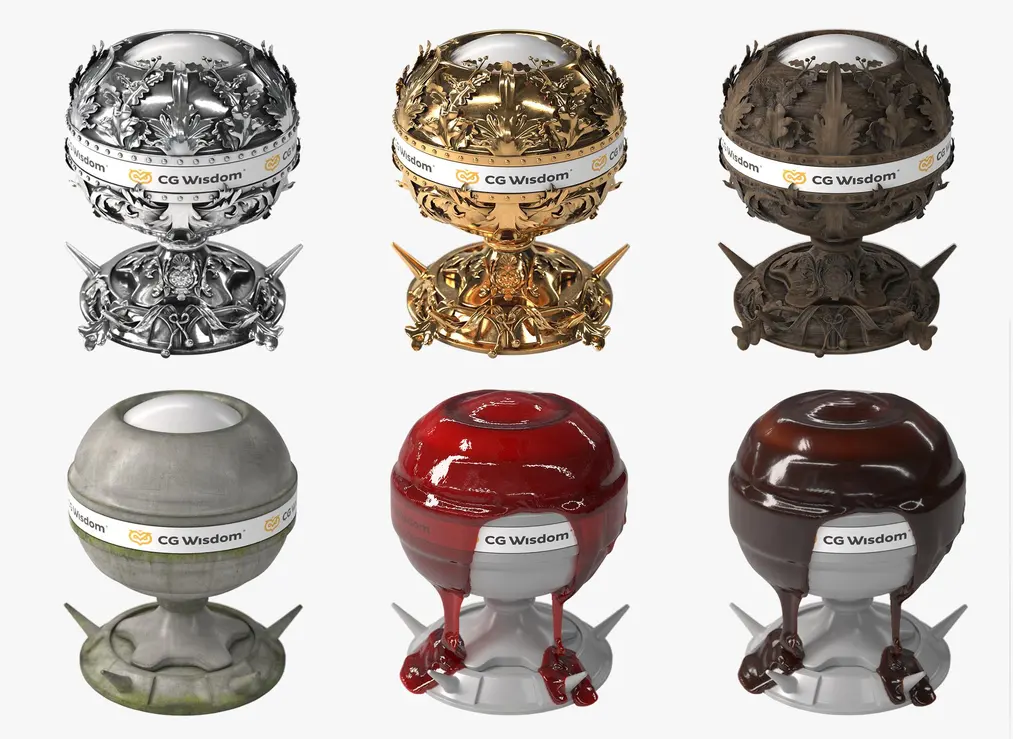
In 3D graphics, texture refers to a digital image that is applied to the surface of a 3D model. Textures can mimic the appearance and feel of various materials such as wood, fabric, metal, leather, and many others. The use of textures allows for realistic details such as patterns, shininess, roughness, and light reflections.
Example set of textures for a brick wall: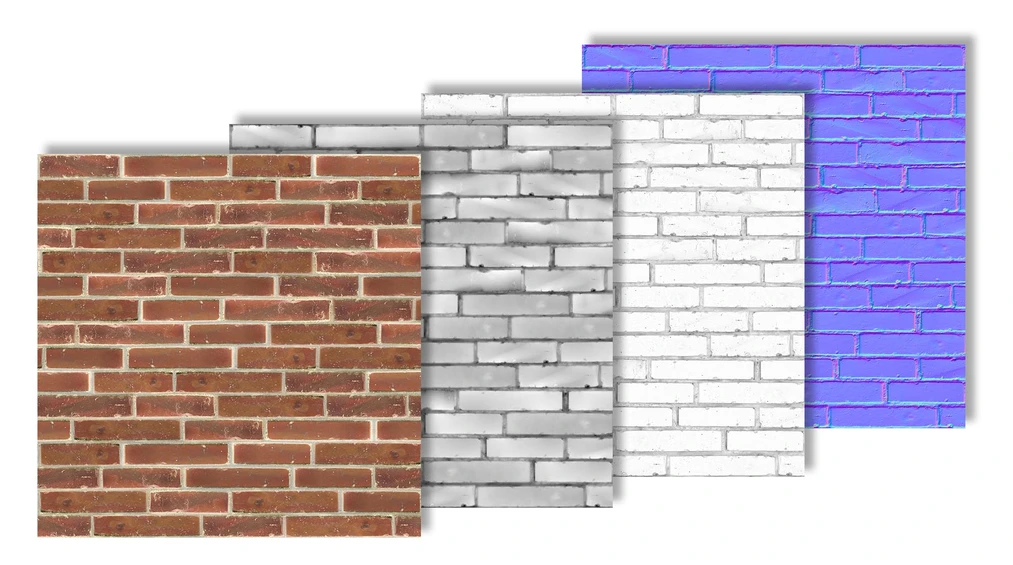
Types of Textures
- Bitmaps: also known as raster graphics, are a type of computer graphics consisting of a grid of pixels. Each pixel in a bitmap has a specific color, and together they form a complete image. Bitmaps are one of the most basic and widely used graphic formats in the digital world, utilized in both simple graphics and complex digital images.
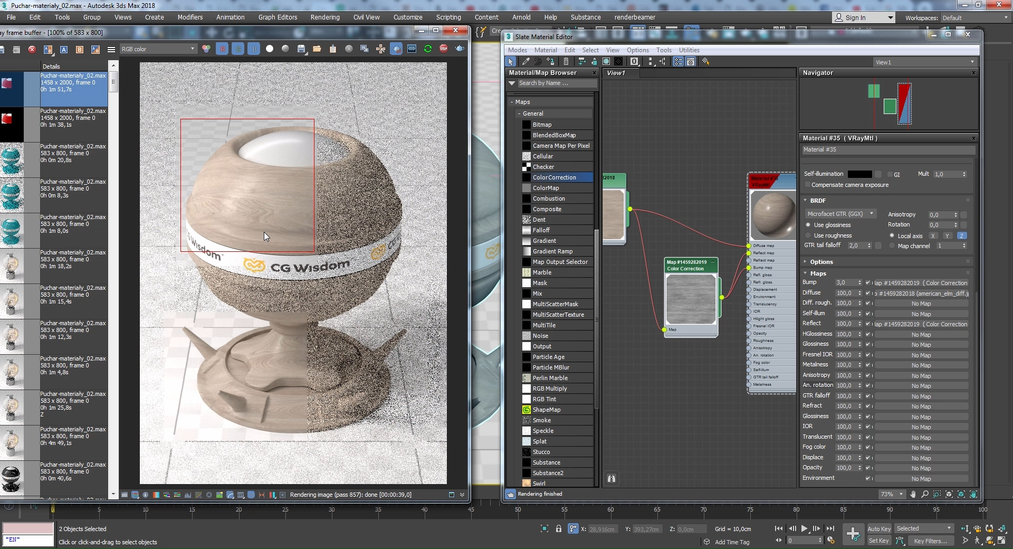
Example of using a texture in the process of creating wood material
- Procedural Textures: are mathematically generated by the computer. They allow for creating more complex patterns and effects, which can be difficult or impossible to achieve using bitmaps. They are often used to create natural patterns such as wood, marble, or clouds.
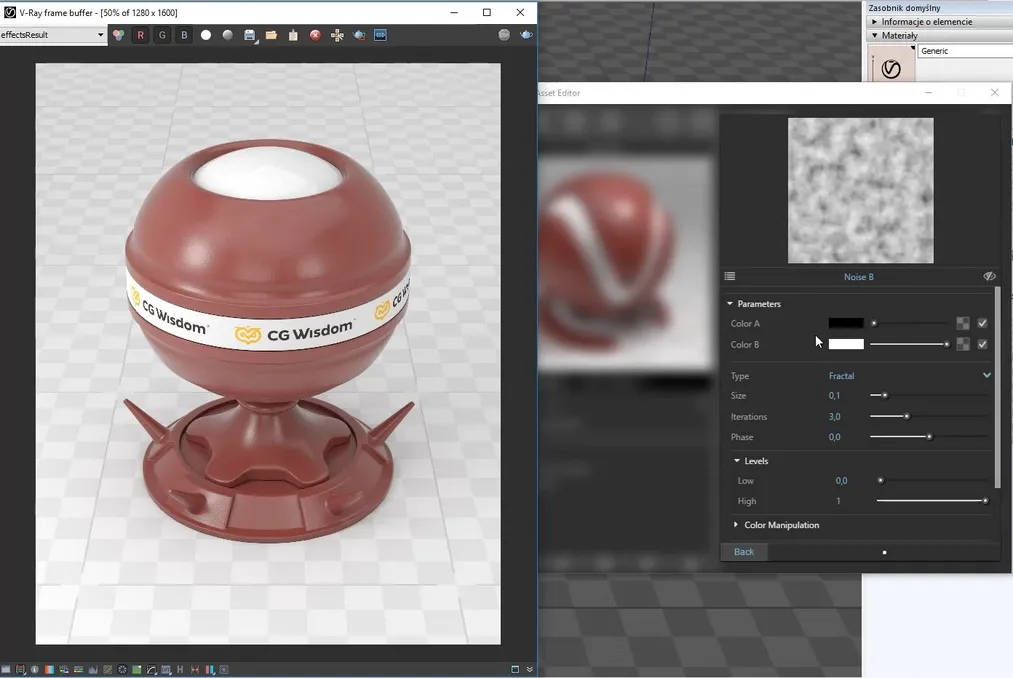
Example of using procedural texture - Noise in Bump map to achieve an uneven surface effect.
Main Features of Bitmaps
- Resolution-dependent: The quality of a bitmap image is directly related to its resolution, i.e., the number of pixels per unit area. Higher resolution means higher detail and better image quality.
- Pixel-Level Editing: Bitmaps allow editing at the level of individual pixels, providing great control over each detail of the image.
- Usage in Textures: In 3D graphics, bitmaps are often used as textures applied to 3D models. Due to their detail and flexibility, they allow realistic representation of various materials and surfaces.
Main Features of Procedural Textures
- Dynamic Generation: Procedural textures are created in real time by graphics software, allowing for great flexibility and adaptability to different project requirements.
- High Scalability: As they are mathematically generated, procedural textures are not limited by resolution and can be scaled to any size without loss of quality.
- Complex Patterns and Effects: Procedural algorithms allow for creating a wide range of patterns - from natural-looking textures such as wood, stone, clouds, to more abstract patterns and effects.
- Memory Efficiency: Procedural textures often occupy less disk space than bitmap equivalents, as they are stored as sets of rules and procedures, rather than as a large number of pixels.
Creating Textures Step by Step
- Gathering Materials: The first step in creating textures is gathering the appropriate materials. You can use your own photos or find images in online databases. It is important that the materials are of high quality and accurately represent the properties of the material being simulated.
- Editing and Adjustment: After gathering materials, the next step is their editing. Programs such as Adobe Photoshop offer a wide range of tools for texture editing. You can adjust the color, contrast, saturation, and transform images into tiles that can be repeated on surfaces without visible seams.
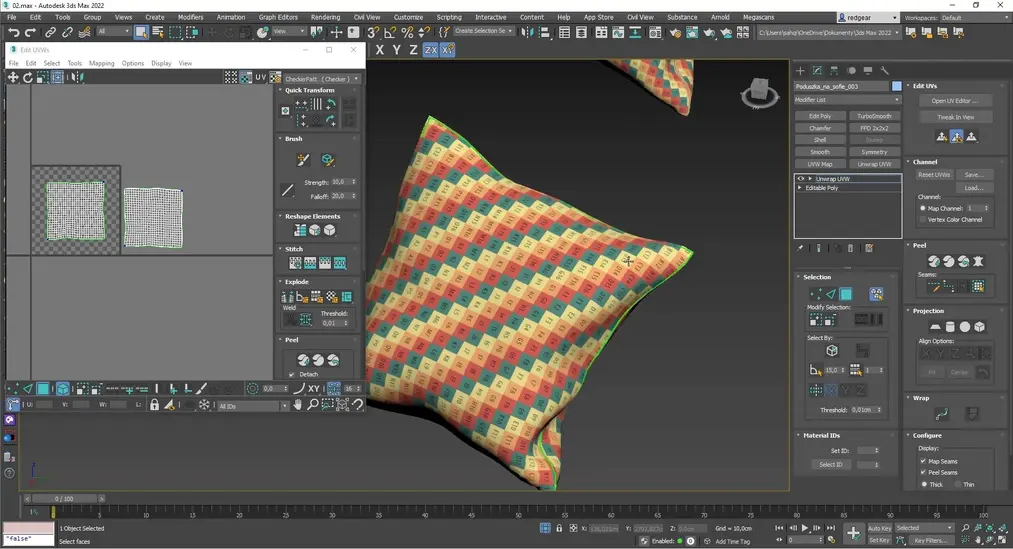
- Texture Mapping: In 3D modeling programs, textures need to be mapped onto the model. This is the process of determining how the texture will be placed on the object's surface. Texture mapping can be complex, especially on complex surfaces, and requires skill and experience. If you're interested in this topic, check out our course - 3ds Max - Fundamentals of Texturing - Unwrap UVW
- Special Effects: To make textures more realistic, additional maps such as reflection, specular, glossiness, bump, displacement, and many others can be added.
Advanced Textures and Their Use
- 3D Painting: Modern 3D graphics software offers tools for direct painting on 3D models. This allows for precise addition of details and texture corrections directly on the model.
- HDR and Lighting: High-quality textures often require advanced lighting. The use of HDR (High Dynamic Range) and other lighting techniques can significantly affect how the texture is perceived on the model.
- Texture Optimization: When creating graphics for games or VR/AR applications, texture optimization is important. This includes reducing the texture file size while maintaining quality and ensuring that textures look good in different lighting conditions.
Summary
Textures are an integral part of computer graphics, particularly in interior design and architecture. By appropriately using and creating textures, the quality and realism of visualizations can be significantly enhanced. At cgwisdom.pl, we offer courses that cover both the basics and advanced techniques of creating textures, allowing our students to master this key skill in 3D graphics.
Read on our blog
-
![How to create realistic materials in SketchUp - what are PBR maps?]()
How to create realistic materials in SketchUp - what are PBR maps?
Do you want to create realistic materials in V-Ray for SketchUp? Use Diffuse, Normal or Displacement maps to elevate the quality of your visualizations! -
![SketchUp - how to fix invisible .skp icon previews?]()
SketchUp - how to fix invisible .skp icon previews?
Having trouble with invisible .skp file icon previews in SketchUp? Learn how to quickly fix this issue and why it happens. Check out the solution! -
![Why SketchUp Is the Best Program for Interior Design?]()
Why SketchUp Is the Best Program for Interior Design?
See how SketchUp makes 3D interior design easier – from an intuitive interface to photorealistic renderings and rich libraries of ready-to-use models! -
![SketchUp - Advantages and Limitations]()
SketchUp - Advantages and Limitations
Discover the pros and cons of the most popular interior design software!